-
Diffusion through Permutation30 pts · 10401 Solves · 25 SolutionsWe've seen how S-box substitution provides confusion. The other crucial property described by Shannon is "diffusion". This relates to how every part of a cipher's input should spread to every part of the output.
Substitution on its own creates non-linearity, however it doesn't distribute it over the entire state. Without diffusion, the same byte in the same position would get the same transformations applied to it each round. This would allow cryptanalysts to attack each byte position in the state matrix separately. We need to alternate substitutions by scrambling the state (in an invertible way) so that substitutions applied on one byte influence all other bytes in the state. Each input into the next S-box then becomes a function of multiple bytes, meaning that with every round the algebraic complexity of the system increases enormously.
An ideal amount of diffusion causes a change of one bit in the plaintext to lead to a change in statistically half the bits of the ciphertext. This desirable outcome is called the Avalanche effect.
The ShiftRows and MixColumns steps combine to achieve this. They work together to ensure every byte affects every other byte in the state within just two rounds.
ShiftRows is the most simple transformation in AES. It keeps the first row of the state matrix the same. The second row is shifted over one column to the left, wrapping around. The third row is shifted two columns, the fourth row by three. Wikipedia puts it nicely: "the importance of this step is to avoid the columns being encrypted independently, in which case AES degenerates into four independent block ciphers."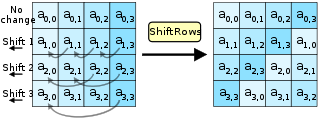
The diagram (and the AES specification) show theShiftRowsoperation occuring in column-major notation. However, the sample code below uses row-major notation for the state matrix as it is more natural in Python. As long as the same notation is used each time the matrix is accessed, the final result is identical. Due to access patterns and cache behaviour, using one type of notation can lead to better performance.
MixColumns is more complex. It performs Matrix multiplication in Rijndael's Galois field between the columns of the state matrix and a preset matrix. Each single byte of each column therefore affects all the bytes of the resulting column. The implementation details are nuanced; this page and Wikipedia do a good job of covering them.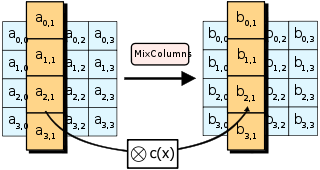
We've provided code to perform MixColumns and the forward ShiftRows operation. After implementinginv_shift_rows, take the state, runinv_mix_columnson it, theninv_shift_rows, convert to bytes and you will have your flag.
Challenge files:
- diffusion.py
You must be logged in to submit your flag.
Level Up

You are now level Current level